CM/Archive
CM/Archive is a ConSol CM add-on which allows to archive tickets from ConSol CM. It is a separate Java web application with a MongoDB database.
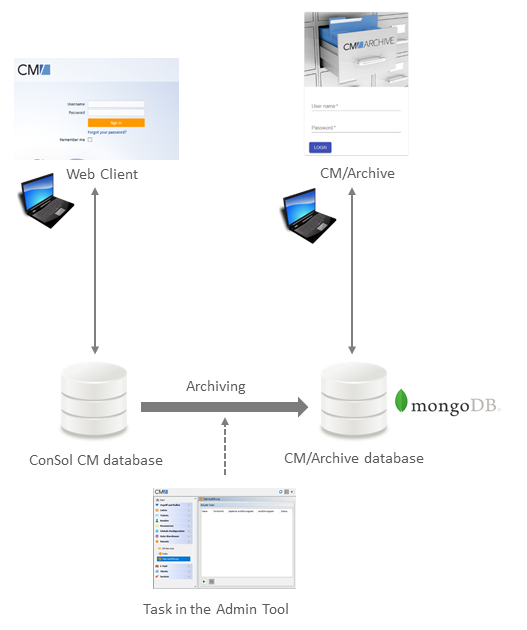
The following figure illustrates how CM/Archive integrates with ConSol CM.
Figure 3: Architecture of ConSol CM with CM/Archive
Requirements for CM/Archive
The following system requirements apply for CM/Archive:
- ConSol CM version 6.11.2.1 and up
- MongoDB version 3.6
- Java 1.8
Please also see the official system requirements on the TecDoc server.
Installing CM/Archive
The following steps are required to install CM/Archive:
- Installing and setting up the MongoDB database
- Setting the system properties for CM/Archive in the Web Admin Suite
- Setting the properties for the CM/Archive application
- Starting CM/Archive
Preliminary note
The CM/Archive application is delivered with three modes: production mode, demo mode and developer mode. This manual covers the installation in production mode, as the other modes should be used only for testing purposes.
Installing and setting up the MongoDB database
The first step is to install the MongoDB. You can find a detailed description in the respective MongoDB documentation for your operating system:
- Linux: Install MongoDB on Linux
- Windows: Install MongoDB on Windows
The next step is to configure the CM/Archive user with the corresponding authentication. Please proceed as follows:
-
Start the MongoDB instance without authentication
Use the following command to start the MongoDB instance without authentication:
mongod --port 27017 --dbpath /data/archive
The mongod options have the following meaning:
- --port: Indicates the database connection port. The default value is 27017.
- --dpath: Defines the directory where the MongoDB instance stores its data. The default value is /data/db on Linux and macOS, and \data\db on Windows.
- --bind_ip: Use this option to provide the IP address if you want to change the default value (localhost, 127.0.0.1).
Please see the mongod documentation for further information about the options.
-
Connect to the MongoDB instance
Use the following command to connect to the MongoDB instance:
mongo --host 127.0.0.1:27017
The following output should be displayed:
MongoDB shell version v3.6.4
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 3.6.4
>
-
Create the administrator user
The administrator user has to be created in the admin database with the role userAdminAnyDatabase. The administrator user has only permissions to create and manage users and roles. It cannot be used for any other operations, e.g., reading data. The following command can be used to create the administrator user:
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "admin",
pwd: "consol",
roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ]
}
)
-
Restart the MongoDB instance with access control
Disconnect the MongoDB shell and restart it with the --auth option or, if you use a configuration file, the security.authorization setting. The following command can be used to restart the MongoDB instance:
mongod --auth --port 27017 --dbpath /data/archive
Clients that connect to this instance must now authenticate themselves as a MongoDB user. They can only perform actions as determined by their assigned roles.
-
Connect with the administrator user
Use the following command to connect to the MongoDB instance with the above created administrator user:
mongo --host 127.0.0.1:27017
use admin
db.auth("admin", "consol")
-
Create the CM/Archive user
Create the CM/Archive user archive with the database archivedb using the db.createUser() command. The user needs to have the readWrite role, as shown in the following example:
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "archive",
pwd: "consol",
roles: [ { role: "readWrite", db: "archivedb" } ]
}
)
-
Connect with the CM/Archive user
Use the following command to connect to the MongoDB instance with the above created CM/Archive user:
mongo --host 127.0.0.1:27017
use admin
db.auth("archive", "consol")
use archivedb
Setting the system properties for CM/Archive in the Web Admin Suite
The system properties for CM/Archive are managed in two modules in the Web Admin Suite:
cmas-archive-core-server:
- archive.uri
URL from which the CM/Archive application can be accessed.
cmas-auth-server:
- access.token.signing.key
Secret shared between the authorization server and client application using OAuth2, needs to match archive.oauth2.access.token.signing.key in the configuration file. - client.archive.access.token.validity.seconds
- client.archive.refresh.token.validity.seconds
- client.archive.secret
Secret shared between the authorization server and CM/Archive, needs to match archive.oauth2.client.secret in the configuration file.
Setting the properties for the CM/Archive application
Some properties for the CM/Archive application need to be provided in a properties file which has to be saved in the same directory as the war file of CM/Archive.
The name of the properties file is archive-prod.properties. It has to contain the following settings:
archive.cm6.endpoint=http://127.0.0.1:8888
archive.oauth2.access.token.signing.key=94623427-5a74-11e8-a6eb-6127838b1c93
archive.oauth2.client.secret=94623428-5a74-11e8-a6eb-6127838b1c93
archive.mongodb.database.name=archivedb
archive.mongodb.uri=mongodb://archive:consol@127.0.0.1:27017/?&journal=true&w=majority&maxPoolSize=1000
The following list states the meaning of the properties:
- archive.cm6.endpoint
This is the URL and port where the ConSol CM instance is executed. - archive.oauth2.access.token.signing.key
Secret shared between the authorization server and client application using OAuth2, needs to match the ConSol CM system property cmas-auth-server, access.token.signing.key - archive.oauth2.client.secret
Secret shared between the authorization server and CM/Archive, needs to match the ConSol CM system property cmas-auth-server, client.archive.secret - archive.mongodb.database.name
This is the name of the MongoDB database as created in step 6 above. - archive.mongodb.uri
User name and password of the CM/Archive user, and URL of the MongoDB instance
Starting CM/Archive
Start CM/Archive using the following command:
java -jar archive-6.11.2.9.war --spring.profiles.active=prod
By default, CM/Archive starts on port 8080. You can choose a different port by adding, e.g., --server.port=8090 to the command.
You can also create a start script for CM/Archive. The following example shows a start script for Linux operating systems.
#!/bin/bash
ARCHIVE_WAR=${ARCHIVE_WAR:-'archive-6.11.2.9.war'}
ARCHIVE_PROPERTIES=${ARCHIVE_PROPERTIES:-'--spring.profiles.active=prod'}
ARCHIVE_PIDFILE=${ARCHIVE_PIDFILE:-'archive.pid'}
ARCHIVE_JAVA=${ARCHIVE_JAVA:-'java'}
cd "$(pwd)/$(dirname "$0")" || exit 1
start()
{
if [ -f "$ARCHIVE_WAR" ]; then
if [ -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" ]; then
local pid
pid=$(cat "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE")
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf 'Archive is already running\n'
return 0
fi
fi
printf 'Starting archive...'
"$ARCHIVE_JAVA" -jar "$ARCHIVE_WAR" $ARCHIVE_PROPERTIES > /dev/null 2>&1 &
printf '%s' "$!" > "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" || return 1
sleep 1
if [ -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" ]; then
local pid
pid=$(cat "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE")
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf 'done\n'
return 0
fi
fi
printf 'failed\n';
rm -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE"
else
printf 'Archive war file %s has not been found in %s\n' "$ARCHIVE_WAR" "$(pwd)"
fi
return 1
}
stop()
{
if [ -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" ]; then
local pid
pid=$(cat "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE")
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf 'Stopping archive...'
kill "$pid" || return 1
for i in {1..60} ; do
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf '.'
sleep 1
else
break
fi
done
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf 'killing...'
kill -9 "$pid" || return 1
fi
printf 'done\n'
rm -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" || return 1
return 0
fi
fi
printf 'Archive is stopped\n'
}
status()
{
if [ -f "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE" ]; then
local pid
pid=$(cat "$ARCHIVE_PIDFILE")
if [ "$(ps -o pid= -p "$pid")" = "$pid" ]; then
printf 'Archive is running\n'
return 0
fi
fi
printf 'Archive is stopped\n'
return 1
}
case "$1" in
'start')
start
;;
'stop')
stop
;;
'status')
status
;;
'restart')
stop && start
;;
*)
printf 'Usage: %s start|stop|status|restart\n' "$0"
;;
esac
Code example 2: Start script archive.sh for CM/Archive on Linux
Please note that execute permissions are needed for the script file:
chmod +x archive.sh
You can start, stop and restart CM/Archive with the following commands:
./archive.sh start|stop|status|restart