Open topic with navigation
Customer Relations
Introduction
Customer Relations represent relations between customers (Data Objects), i.e., companies and contacts. They can be one of two types:
- directional (different levels in a hierarchy)
- reference (same level, no hierarchy)
A relation is of one of the following types:
- company - company
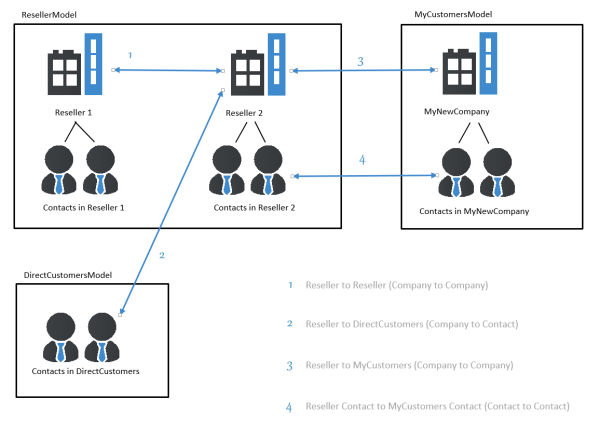
e.g., ... has a cooperation with ... (company X cooperates with company Y)- The companies can belong to the same or to different customer groups.
- The involved customer groups can have the same or different customer data models.
- company - contact
e.g., ... is customer of ... (contact X is customer of company Y)- The company and the contact can belong to the same or to different customer groups.
- The involved customer groups can have the same or different customer data models.
- contact - contact
e.g., ... is serviced by ... (contact X from company X is serviced by contact Y from company Y)- The companies and contacts can belong to the same or to different customer groups.
- The involved customer groups can have the same or different customer data models.
Figure 258: ConSol CM FlexCDM - Examples of customer relations
Management of Customer Relations Using the Admin Tool
To make Customer Relations available to the engineers, the relations have to be defined in the Admin Tool. Open the navigation item Relations in the navigation group Customers. All relations are listed, new relations can be added, and old ones can be deleted.
Figure 259: ConSol CM Admin Tool - Managing customer relations
The following elements are available:
- List of relations
- Filter
- Filter for an expression which has to be entered into the field Filter. Use the asterisk as a placeholder for any character.
- Filter for customer groups using the drop-down menu.
- Add button
Add a new relation. The pop-up window Create data object relation (see next section) is opened.
- Edit button
Modify the parameters of a relation. The pop-up window Edit data object relation (see next section) is opened.
- Delete button
Delete an existing relation. This is only possible when no relations of this type have been set (using the Web Client).
- Change order (arrows up and down)
Place a relation at a specific position in the list. This defines the order of the manual relations as they are displayed in the Web Client.
- Activate / deactivate relations
A deactivated relation is not available in the Web Client, i.e., a relation of this type can no longer be created. Existing relations of this type are not modified and are displayed in the GUI.
Figure 260: ConSol CM Admin Tool - Details of a customer relation
To create a new relation, use the Add button, to edit a relation use the Edit button. In both cases, the detail information pop-up window for a relation is opened where you can edit the following fields:
- Name
Name of the relation. The technical name is used for internal use cases (scripts) whereas the localized name will be displayed in the Web Client (as for most fields in ConSol CM). For details about localization, please refer to section Localization of Objects in General, Type 1.
- Type
Select one of the two types:- Directional
A directional relation has a defined source and a defined target. A Data Object can be source and target for different relation types at the same time. An example for a directional relation is a reseller (company) to end customer (contact) relation: sells products to. A company (reseller) sells products to a contact (end customer). A relation between two contacts of a company: is boss of. The other direction, works for, can also be used, but designing a consistent structure for the entire system, to avoid misunderstandings, is highly recommended. - Reference
A reference is an undirected relation with no hierarchical implications, e.g., has a cooperation with.
- Reportable
Defines if the relations of this type should be transferred to the data warehouse.
- Only configurable via workflow
If this checkbox is marked then the relation is not available in the Web Client but can only be created via workflow scripts. Such relations cannot be manipulated manually.
- For a directional relation select:
- Source
- Level
Level of the relation source, i.e., company or contact or any (choose the latter if the source can be either a company or a contact). - Customer group
The customer group of the source Data Object. - Description
Will be displayed in the Web Client as the description of the relation on the source side.
- Target
- Level
Level of the relation target, i.e., company or contact or any (choose the latter if the target can be either a company or a contact). - Customer group
The customer group of the target Data Object. - Description
Will be displayed in the Web Client as the description of the relation on the target side.
Creating Customer Relations Using the Web Client
In spite of this being an administrator's manual, we will show you how relations are set using the Web Client, because, as an administrator, you should always know what the consequences of administration modifications are.
As an engineer who has the access permissions to the source and to the target customer group, you can add a relation of one Data Object to another in the Relations section of the source Data Object. You have to have at least one role with the access permission Write for the source customer group and the target customer group to perform this operation. You can set the relations on the Data Object-specific page, i.e., open the company page or the contact page of the potential source object.
For example, you can create a relation Sells products to from a company in the Reseller customer group to a contact in the Direct customers customer group. Of course, this relation has to be defined in the Admin Tool first. Use the Add link in the Relations section and then select the relation from the drop-down menu. Enter the target name (e.g., contact name) in the auto-complete text field. You can also add a note. Then click OK. The relation can be edited or deleted afterwards using the respective links (Edit, Remove).
Please refer to the ConSol CM User Manual for a detailed explanation of working with customer relations.
Figure 261: ConSol CM Web Client - Setting a relation
Scripting Using Relations
A new class, the UnitRelationService, is available. For details please refer to the ConSol CM API Java Doc.
In this book we will use the terms customer and customer definition. However, the corresponding scripts use the term data object and the names of the corresponding Java classes are Unit and UnitDefinition. All other Java classes which deal with customer objects are also still named Unit... Please keep that in mind if you work as both a ConSol CM administrator and programmer. Please refer to the ConSol CM Java API Doc for details.
// Creates the unit relation
UnitRelation create(UnitRelation pUnitRelation)
// Deletes the unit relation
void delete(UnitRelation pUnitRelation)
// Get a set of relations by criteria
PageResult<UnitRelation> getByCriteria(UnitRelationCriteria pCritieria)
// Gets unit relations by source and target units
Set<UnitRelation> getBySourceAndTarget(Unit pSourceUnit, Unit pTargetUnit)
// Gets unit relations by source or target units
Set<UnitRelation> getByUnits(Collection<Unit> pUnits)
// Updates the unit relation
void update(UnitRelation pUnitRelation)
Please refer to the ConSol CM Process Designer Manual for a detailed explanation on how to write scripts which use Customer Relations.
Data Object (Customer) Relations to Resources
The relations of resources to contacts or to companies are always defined as Resource Relations, i.e., defined for resources, not for Data Objects. The company or contact objects are assigned as potential target objects when the Resource Relation is defined. Resource Relations are explained in section CM.Resource Pool - Resource Relations.