Action scripts
Actions scripts are used to add logic to actions which can be executed for contacts, resources and search results. Optionally, actions can have condition scripts which determine the availability of the action. If a condition script is defined for the action, the action is only available if the condition script returns true. For manual actions, this means that the action is not displayed in the Web Client. For automatic actions, this means that the action script is not executed.
Background knowledge about actions
Actions are available for three types of objects:
- Contacts
Actions for persons or companies, see Contact actions. - Resources
Actions for resources, see Resource actions. - Search results
Actions for cases, contacts or resources which belong to the result of a detailed search, see Search actions for cases, Contact actions and Resource actions.
Actions for cases are called workflow activities. They are implemented in Scripts of the type Workflow.
Actions can be of the following types:
- Automatic actions
Automatic actions are performed by the system whenever the situation for which they are defined occurs in an object. The following automatic actions are available:- Create: Action performed when an object is created.
- Update: Action performed when an object is modified.
- Delete: Action performed when an object is deleted.
- Relation: Action performed when a relation to an object is created or deleted (changes to the comment of a relation are not considered). If both the source and the target object of a relation belong to a type with a relation action, two relation actions are executed.
- Manual actions
Manual actions are performed by a user who clicks the respective action in the Web Client. There are two types of manual actions:- Manual: Action performed for a single object.
- Search: Action performed for the results of a detailed search. This can be one or several cases, contacts or resources. The action is performed only for the objects which are displayed on the current page of the results table. If the page customization attribute enableRowSelection from the type detailSearch is set to “true”, the user can select the objects for which the action should be performed.
Manual actions can have forms which are opened when the user clicks the action in the Web Client. They need to be filled out to complete the action, see Action forms.
Available action script types
The script type which is used for action scripts depends on the usage of the script. The following script types are available:
- Action form condition:
Script which determines if an action form is displayed. - Action form prefill:
Scripts which fills the fields of an action form with predetermined values. - Contact action:
Script which implements the logic of an action executed for a contact. - Contact condition:
Script which determines if a contact action is available. - Resource action:
Script which implements the logic of an action executed for a resource. - Resource condition:
Script which determines if a resource action is available. - Search action for cases:
Script which implements the logic of an action executed for the results of a case search. - Search action for contacts:
Script which implements the logic of an action executed for the results of a contact search. - Search action for resources:
Script which implements the logic of an action executed for the results of a resource search. - Search condition for cases:
Script which determines if a search action for case results is available. - Search condition for contacts:
Script which determines if a search action for contact results is available. - Search condition for resources:
Script which determines if a search action for resource results is available.
Logic of action scripts
The logic of an action script usually covers two aspects:
- Modify the current object or an related object, see Working with the current object.
- Determine what should happen after performing the action, see Defining the behavior after the action.
If the script is used as a condition script, it has the following purpose:
-
Manual actions: Determine whether the action is displayed in the Web Client.
-
Automatic actions: Determine whether the action script is executed.
-
Action forms: Determine whether the action form is displayed.
For update actions, you need to make sure that the action script code does not cause an infinite loop. This could happen, for example if you call the method unitService.update(Unit) in a contact update script.
Working with the current object
The object for which the action is executed is implicitly available in the script. This allows updating the object or performing any other relevant action. The following objects are available:
- Contact action: unit, contact, company, formFields (if an action form is used), controlForm (if an action form is used)
- Resource action: resource, formFields (if an action form is used), controlForm (if an action form is used)
- Relation action: relation for all relations except for case-contact relations, role (for case-contact relations only), actionType (possible values: ADD if the relation has been added, or REMOVE if the relation has been removed), ticket |resource |unit (if such an object is part of the relation)
- Update action: changes (class UnitChanges or ResourceChanges)
- Delete action: deleteType (for contact actions only, possible values: delete or delete_all)
- Search action for cases: tickets for search results, ticket (if an action form is used)
- Search action for contacts: units for search results, contact and company (if an action form is used)
- Search action for resources: resources for search results, resource (if an action form is used)
Defining the behavior after the action
In all action scripts, the behavior of the system after completing the action can be defined by using methods of the class OperationResponseBuilder. An object of this class, named client, is implicitly available in all action scripts, in automatic as well as in manual scripts. This object is also available in workflow scripts.
The client object includes methods for the following operations:
- open a certain URL
- open the page to create a case (with or without contact), contact or resource
- open the page of a case, contact or resource (with or without displaying a form)
- display a success or error message
- rollback the changes made in the action script
- open CM/Doc
Please refer to the ConSol CM API documentation for details about the available methods.
Defining the binding of action forms
Auto-binding allows to use action forms to directly manipulate the values of the original object, i.e. the case, contact or resource for which the form is opened. Upon saving the form, the original object is modified automatically. Use client.goToUnit(contact) or client.goToResource(resource) to reload the Web Client page to display the values changed in the form.
By default, auto-binding is enabled if the action does not have an action script. Otherwise, you need to enable it in the script by adding the following code:
def isAutoBindingEnabled() {
return true;
}
You can disable auto-binding by returning “false”. If auto-binding is disabled, changes made in the form are not saved to the object.
Coding examples
Opening the page to create a case
Use one of the following methods:
- client.goToCreateTicket(ticket)
- client.goToCreateTicket(ticket).withCustomer(unit)
The following example opens the page to create a case. The queue “Helpdesk” is preselected and some fields are prefilled.
import com.consol.cmas.common.model.ticket.Ticket
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
ticket.setQueue(queueService.getByName("Helpdesk"))
ticket.setSubject("sample subject")
ticket.set("queue_fields.string", "test")
client.goToCreateTicket(ticket)
//to additionally set the main contact use withCustomer()
//client.goToCreateTicket(ticket).withCustomer(unit)
Code example 1: Open the page to create a case
Opening a case and displaying an activity form
Use the following method:
- client.goToTicket(ticket).openActivityForm("activity path")
The following example opens the case with the name “100270” and directly opens the activity form of the Dismiss ticket activity.
client.goToTicket("100270").openActivityForm("defaultScope/Service_Desk/Ticket_dismissed/Dismiss_ticket_")
Code example 2: Open a ticket page with an ACF
Displaying messages in the Web Client
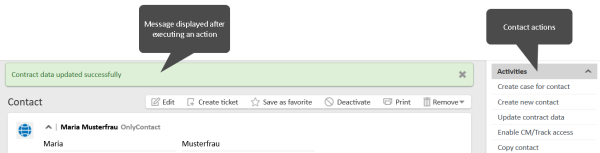
You can display messages with either a green or a red background.
The following methods display a message with a green background. The message text can be provided as a string or label:
- client.success()
- client.showInfoMessage(string or label)
- client.showMessage(string or label)
- client.showMessage(String pMessageKey, OperationMessage.Severity.INFO)
The following methods display a message with a red background. The message text can be provided as a string or label:
- client.failure()
- client.showErrorMessage(string or label)
- client.showDebugMessage(string or label)
- client.showMessage(String pMessageKey, OperationMessage.Severity.WARN)
By default, the methods to show messages do not refresh the page. Therefore, any updates to the object performed within the action scripts are not yet visible when the message is displayed. You can append withRefreshContent() to the method to refresh the page before showing the message:
client.showMessage("controlForm.info.executionOK").withRefreshContent()
The following figure shows a message with a green background: