Introduction to ConSol CM
Purpose and usage of ConSol CM
ConSol CM is a process management platform suitable for a huge variety of business processes. The products CM/Ticketing, CM/Helpdesk and CM/Complaint are based on the platform and provide ready-to-use processes for handling customer inquiries, support requests and complaints. If you have purchased one of these three standard products, you can directly work with the processes or adapt them to your needs. Alternatively, you can use the platform to implement new processes which are tailored specifically to your use cases and requirements. The powerful workflow editor allows you to decide if the process flow should be rather strict or the users should have more flexibility.
ConSol CM include many features to enable communication and interaction. In addition to the Web Client, used for the internal handling, ConSol CM also comes with the customer portal CM/Track and various interfaces and add-ons which facilitate additional features as reporting or integration with other IT systems.
System components of ConSol CM
ConSol CM comprises different client applications. Depending on your roles and tasks in your company you will use one or more of those applications. The following figure shows the most important ones:
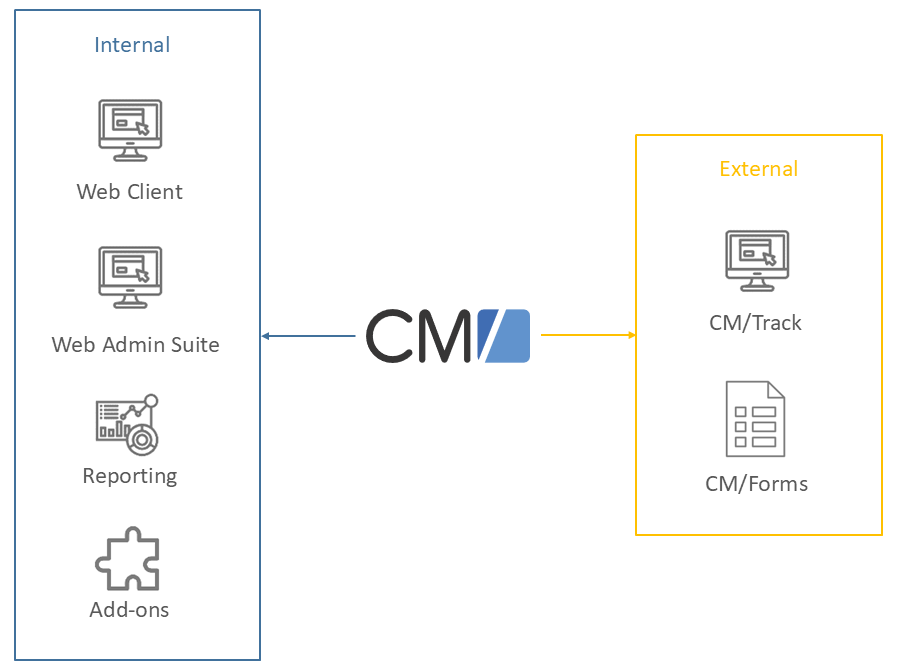
- Web Client: The Web Client is the primary access point to the system for internal users. They work with cases, contacts and resources.
- Web Admin Suite: The Web Admin Suite is used by administrators for setting up and maintaining the system. This includes both the system configuration and the workflows.
- Reporting: ConSol CM comes with a data warehouse to consolidate data for reporting purposes. In addition, you can create dashboards using scripts, or purchase the add-on CM/EBIA for report creation using a graphical user interface.
- Add-ons: ConSol CM comes with a number of add-ons which can be licensed separately to provide additional features, as for example an archive or machine learning.
- CM/Track: CM/Track is a portal which is the primary access point to the system for external users, either your customers or colleagues who do not work with the Web Client. CM/Track is an add-on which requires a separate license.
- CM/Forms: CM/Forms is an add-on which allows to manipulate ConSol CM objects via web forms. The web forms can be filled by unauthenticated users.
Furthermore, ConSol CM is not an isolated application but can be easily integrated into your company's IT infrastructure, e.g. using webhooks or the REST interface.
See Architecture for a complete list of extensions and third-party integrations.
Technical principles of ConSol CM
The following objects are essential when working with ConSol CM:
- Users: Users are the internal people who work with the system. They work on cases to carry out the tasks defined in the business process. A case is usually assigned to the user who takes care of it at the moment. There can be only one assignee, but other users, who perform a specific task for the case, can be added as participants. The users have one or several roles which give them access to the system and its objects.
- Contacts: Contacts are the external people whose requests are handled using ConSol CM. They always belong to a customer group which determines the used data model. You can either define simple, one-level models which contain only person data (e.g. name, email address) or complex, two-level models which contain person data (e.g. name, email address) and company data (e.g. address, industry). The permissions to access contact data depend on the customer group. There can be several customer groups and data models.
- Cases: Cases are the requests made by contacts. The users carry out the steps which are defined in the business process to handle the request. The progress, including internal and external communication, is documented in the case. When the request is solved, the case is closed. Closed cases represent a powerful archive and knowledge base. A case can have one main contact and several additional contacts. Each case has a unique number which is used to reference it throughout the system. The key data of a case are shown in its header.
- Queues: Queues contain thematically related cases which should be handled in the same way. They determine if the cases have contacts, how they are processed (workflow), whose cases are processed (customer groups), how the cases should look like (case fields) and who can work on the cases (roles). Queues often reflect the organizational structure of the company. If there are several teams working with different queues, the cases can be passed from one queue to another.
- Workflows: Workflows implement the business process. They consist of several steps, called activities, which need to be performed either manually or automatically to handle the customer requests. The activities are arranged in scopes to illustrate the status of the case. The intelligence of the process, like conditions, decisions, escalations, reminders, or automatically sent emails, is also defined in the workflow. You can implement process chains or a hierarchical process structure by linking several workflows.
- Resources: The ConSol CM add-on CM/Resource Pool allows to manage additional objects which needed in the business process. You are free to define which kinds of resources you need. The resource model defines the corresponding resources types and their data fields.
The case, contact and resource pages include sections with links to the connected objects, so that you can navigate the network easily.
The process intelligence is implemented using scripts. Scripts can be used in the following contexts:
- Workflow: The workflow can include scripts in numerous places. The most important one is the activity script which is executed together with a workflow activity. In addition, scripts can be used in triggers, activity forms and decision nodes for different purposes.
- Actions: Actions are available for contacts, resources and results of the detail search. They can include a script to be run. Contact and resource actions can either be executed manually by the user in the Web Client or automatically when a certain event occurs for the object. Search actions are always executed manually because they become available once the user has performed a detail search in the Web Client.
- Tasks: Tasks allow to execute long-running scripts which are not linked to user actions in the Web Client. They can be useful, for example, for importing data from external systems.